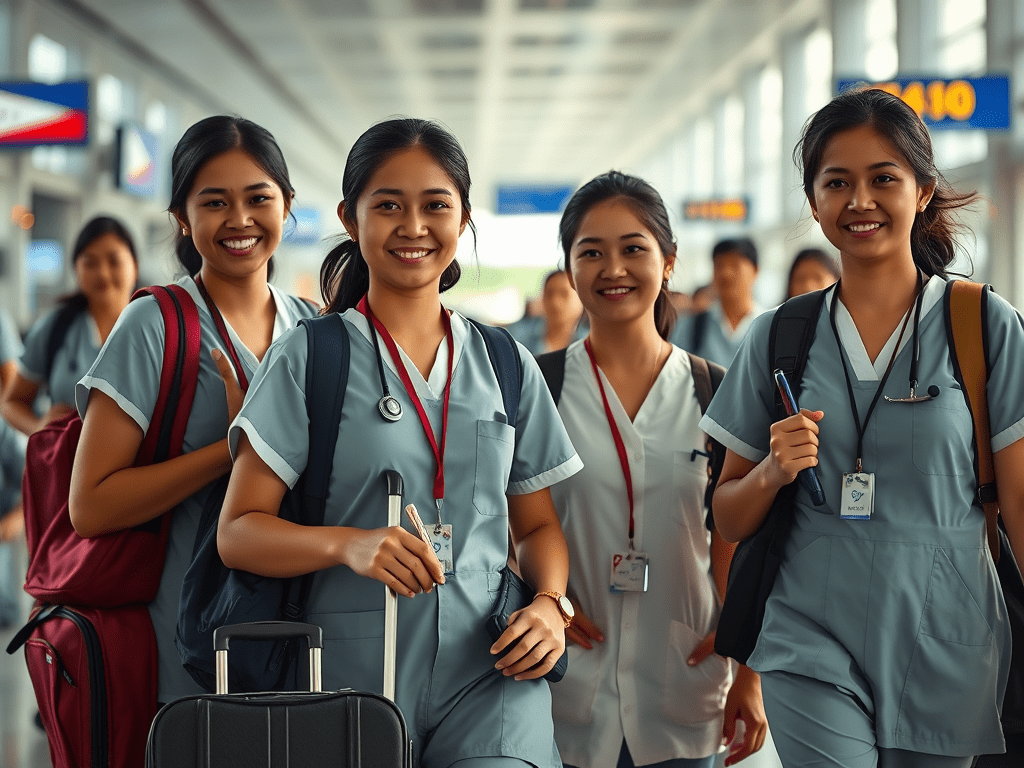
Filipino nurses migrating to better opportunities abroad is contributing to a growing healthcare crisis within the country.
The Philippines has long been known as a global supplier of nurses, with thousands of Filipino nurses working in hospitals around the world. However, in recent years, the country has been grappling with a serious shortage of nurses within its own borders, and the effects are starting to be felt across the healthcare system.
The Nurse Exodus: Why Are Filipino Nurses Leaving?
One of the primary reasons behind the nursing shortage in the Philippines is the increasing number of nurses leaving the country to work abroad. With better pay, career opportunities, and working conditions in countries like the United States, Canada, and the Middle East, many Filipino nurses are opting to seek employment overseas. While this trend has been ongoing for decades, the COVID-19 pandemic further exacerbated the situation, as nurses faced long hours, high stress, and limited personal protective equipment during the height of the crisis.
Despite the country’s reputation as a top exporter of healthcare workers, the demand for nurses domestically has far outstripped supply. Hospitals across the Philippines—especially in rural areas—are struggling to fill nursing positions, with many facilities forced to rely on underqualified staff or offer overtime to existing nurses, further burning them out.
The Impact on Healthcare
The nurse shortage in the Philippines has had significant consequences for the healthcare system. Public hospitals, already underfunded and overwhelmed, are experiencing increased pressure as the patient-to-nurse ratio grows. This leads to longer waiting times, reduced quality of care, and, in some cases, higher patient mortality rates. Moreover, existing nurses are being stretched thin, often working multiple shifts or handling more patients than is safe or sustainable.
In rural areas, the situation is even more dire, with some provinces lacking sufficient healthcare staff to meet the needs of the population. For many Filipinos, especially those in remote areas, access to quality healthcare is becoming increasingly difficult.
Government Initiatives and Challenges
The Philippine government has taken steps to address the shortage, including efforts to improve the wages and working conditions for nurses. In 2021, the government passed an order to increase the salaries of nurses in public hospitals, in hopes of retaining more healthcare workers. However, critics argue that the pay increase still does not reflect the demands of the job, especially when compared to the higher salaries offered abroad.
Moreover, there have been calls for a greater investment in nurse education and training, to ensure that there are enough qualified nurses to meet the growing demand. Some healthcare advocates are also pushing for a re-evaluation of the migration policies that allow nurses to leave the country in large numbers, urging the government to create more incentives for nurses to stay and contribute to the local healthcare system.
Looking Ahead
The nursing shortage in the Philippines is a complex issue that requires urgent attention. While the country has long relied on exporting its nursing talent, it must now find ways to address the gaps within its own healthcare system. As the demand for healthcare services continues to rise, ensuring that the Philippines has a sufficient, well-trained nursing workforce will be key to improving the country’s healthcare outcomes and securing the future of its healthcare system.
Ultimately, without meaningful reforms to improve working conditions, salaries, and opportunities for professional growth, the exodus of nurses is likely to continue, leaving the Philippines to grapple with a healthcare crisis at home.